The motivation behind the Generalized Valence Table (GPT) was to provide a practical tool in chemistry that emphasizes the distribution of electrons into lone pairs and unpaired electrons, rather than relying solely on the identity of the chemical element. The proposed Hybridization-GPT extends this approach by presenting the distribution of hybridization types as a function of the valence and the number of lone pairs on the central atom. In this table, the columns indicate the number of orbitals to be hybridized, which corresponds to the coordination number around the central atom. The nature of the orbital is also taken into account, and this information is conveyed by an offset in each box, shifted to the right and downward. The related Geometry-GPT is also proposed.

Representation of Gillespie nomenclature AnXmEp and corresponding geometry (in red) in the GPT. The column entries represent the coordination number of the central atom.
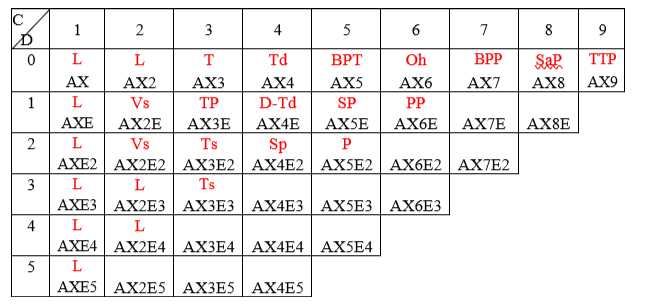
The following shortcuts were used
Linear (L),
Triangular(T)
Tetrahedral (Td)
Trigonal BiPyramidal (TBP)
Octahedral (Oh)
V shaped (Vs)
Trigonal Pyramidal (TP)
distorted Tetrahedral (d-Td)
T shaped (Ts)
Square planer (SP)
square pyramidal (SP)
BiPyramidal Pentagonal (BPP)
Pentagonal (P)
Square antiPrismatic (SaP)
Tricapped Trigonal Prism(TTP)
Laisser un commentaire